During my daily working, I do the development on Windows OS; besides, we have aDebian server for running different jobs automatically, file storage, etc.Sometimes, we also need to transfer files from Windows OS to Linux OS, orreverse; in this case, we use Putty to realize the transfering. Today, I willtalk about how to use Putty for transfer files with the following points:
- What is Putty ?
- Requirements
- Transfering files from Windows to Linux
- Transfering files from Linux to Windows
Yeah, XMODEM is an entire file transfer protocol, and the example code posted has nothing to do with it. Edit: Made dumb suggestion, deleted dumb suggestion. This is what I currently have planned for this in the long run and would like comments if it sounds like a terrible idea. PuTTY xmodem transfering file integration-Send File - Launch rx binary luasenddata('rx -X u-boot.bin',true);- Upload file luaxmodemsnd('D: 00Share u-boot.bin. PuTTY is the CIT-recommended application for secure file transfer using SCP between Windows clients and Windows or Unix servers. Its secure copy utility is called PuTTy Secure Copy Protocol (PSCP). PSCP and PuTTY are available from PuTTY.org. Install PuTTY SCP (PSCP).
What is Putty ?
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator, serial console andnetwork file transfer application. It supports several network protocols,including SCP, SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and raw socket connection. It can alsoconnect to a serial port. The name “PuTTY” has no official meaning.
Requirements
- Windows OS
- Linux OS
- Putty installed: download Putty here
- Putty PSCP installed: download Putty PSCP here
Transfering files from Windows to Linux
To transfer files from Windows OS to Linux OS, we will apply PSCP. Before westart, let’s have a general understanding of it. PSCP means “PuTTy SecureCopy Protocol (PSCP)”, is a tool for transferring files securely betweencomputers using an SSH connection. To use this utility, we should becomfortable working in the Windows Command Prompt.
Now, let’s start to transfer files to Linux:
- Open Windows Command Prompt.
- Type
pscp source_path user_name@host:target_pathat the prompt
Here, ./weekly_report.xlsx specifies the path of source file, xxx is user’saccount for accessing the Linux server, 123.456.789.0 is the host address,/reporting presents target path.
- After the bash script above, we also need to type the password for accessingthe Linux server.
Transfering files from Linux to Windows
Transfering files from Linux OS to Windows OS is similar to the steps above:
- Open Windows Command Prompt.
- Type
pscp user_name@host:source_path target_pathat the prompt
Putty Xmodem Cisco
- Same as above, after the bash script above, we also need to type the passwordfor accessing the Linux server.
Conclusion
In this blog, I introduced how to use Putty to transfer files from Windows OSto Linux OS and reverse. Hope it’s useful for you.
Reference
- “PuTTY”, wikipedia. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PuTTY
- “Transfer Files Using PuTTY”, it.cornell.edu. [Online]. Available: https://it.cornell.edu/managed-servers/transfer-files-using-putty
- Comfreak, “traffic information superhighway”, pixabay.com. [Online]. Available: https://pixabay.com/photos/traffic-information-superhighway-3524185/
Contents
Introduction
This document explains how to recover Cisco Catalyst fixed configuration switches from a corrupt or missing system image or an incorrectly set boot variable. The Catalyst fixed configuration switches that this document describes include the 2940, 2950/2955, 2970, 3550, 3560, 3750 and the 3750 Metro series switches.
Prerequisites
Requirements
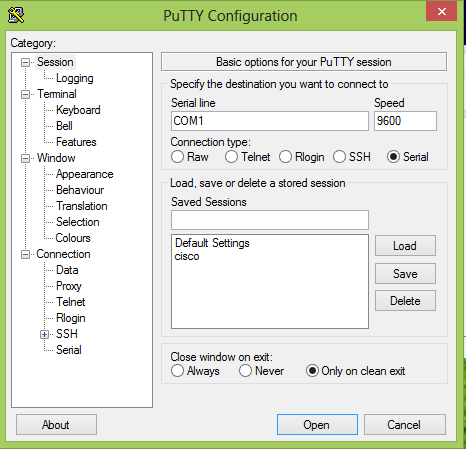
If you have not already done so, connect a PC to the console port of the switch. For information on how to connect a terminal to a Catalyst fixed configuration switch, refer to Connecting a Terminal to the Console Port on Catalyst Switches. Use a terminal emulation program such as Microsoft Windows HyperTerminal in order to establish the console session. These are the settings:
Bits per second: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
Components Used
Putty Xmodem File Transfer Pro
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Conventions
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions.
Problem
When Catalyst fixed configuration switches experience boot errors, these conditions can apply:
The switch is in a continuous reboot.
The switch displays the switch: prompt.
The error loading flash: message appears.
Switch Displays the Switch: Prompt or 'Error Loading Flash:'
The switch: prompt indicates that the switch has not booted completely and requires the user to complete the boot process.
The error loading flash:<image> message indicates that the switch failed to load an image because of a corrupt or missing image.
The corrupt or missing image can be the result of a failed download. In this case, the image has a bad checksum or a failed software upgrade, and the upgrade procedure was not followed properly. There is the possibility that the user deleted the image but did not replace the image. A boot variable can have been set incorrectly.
With a console session open, you see an error message that is similar to this:
Normally, the switch attempts to automatically boot the next valid image in the Flash file system. Here is an example:
If there is no valid backup image from which to boot, the boot process fails completely. Here is an example:
Step-by-Step Recovery Procedure
Use this solution to solve the problem.
Note: A PC must be attached to the console port of the switch, as the Prerequisites section of this document states.
If the switch is in a continuous reboot, complete one of the procedures in this step, which depends on your switch model.
Note: If the switch is not in a continuous reboot, but is already at the switch: prompt, proceed directly to Step 2.
Catalyst 2940 and 2950 series switches
Unplug the power cord.
Hold down the MODE button while you reconnect the power cable to the switch.
The MODE button is on the left side of the front panel.
Release the MODE button after the STAT LED goes out.
Note: The LED position can vary slightly, which depends on the model.
You are now at the switch: prompt.
Proceed to Step 2.
Catalyst 2970, 3550, 3560 and 3750 series switches
Unplug the power cord.
Hold down the MODE button while you reconnect the power cable to the switch.
The MODE button is on the left side of the front panel.
Release the MODE button after the LED that is above Port 1x goes out.
Note: The LED position can vary slightly, which depends on the model.
You are now at the switch: prompt.
Proceed to Step 2.
Catalyst 2955 series switches
Issue a break sequence from the keyboard in order to break into switch: mode.
The terminal application and operating system that you use determine the break sequence to use. HyperTerminal that runs on Windows 2000 uses Ctrl-Break. For more information, refer to Standard Break Key Sequence Combinations During Password Recovery.
This example uses HyperTerminal to break into switch: mode on a 2955:
Proceed to Step 2.
Issue the flash_init command and the load_helper command.
If the Flash has already initialized, you see this:
If the Flash has not initialized, you see this:
Issue the load_helper command in order to load any boot helper images. Here is an example:
Issue the dir flash: command in order to view the contents of the Flash file system.
Determine if there are any Cisco IOS® image files or image directories in flash:. The Cisco IOS image files are .bin files, and the image directories are named with the image filename, excluding the .bin extension. If no Cisco IOS image files or image directories exist, you see this:
If your Flash directory looks like this, proceed directly to Step 4. Step 4 recovers the switch with an Xmodem file transfer.
If there is still an image in Flash, issue the boot command in order to try to recover the switch. Before you issue the boot command, verify where the Cisco IOS image is stored in the Flash directory. The location in which the image is stored can differ, which depends on your switch model.
Catalyst 2940, 2950, and 2955 Flash file system
The Cisco IOS image file (.bin file) always resides in the flash: directory on Catalyst 2940, 2950 and 2955 series switches. Here is an example:
Catalyst 2970, 3550, 3560, and 3750 Flash file system
The organization of the Flash file system on a Catalyst 2970, 3550, 3560, and 3750 is a little different. You can store the Cisco IOS image file in the flash: directory. However, if you use the Cluster Management Suite (CMS) image in order to manage switches with a web interface, you can store the Cisco IOS image file in its own directory. Issue the dir flash:directory command in order to display the image file in this case.
Attempt to Boot the Image
After you have verified where the Cisco IOS image file resides, try to boot the image. Issue either the boot flash:filename command or the boot flash:directory/filename command.
Catalyst 2950
Catalyst 3550
If you issue the boot command and the result is in a successful bootup, either the default switch> prompt or the hostname> prompt displays.
Be sure to verify that you have configured the correct boot statement on the switch. See the Verify section of this document.
If you issue the boot command and the command does not result in a successful bootup, either the switch: prompt displays or you are stuck in a continuous reboot again. The only option to recover the switch is an Xmodem file transfer. Step 4 covers this file transfer.
If the boot command has failed or there is no valid image from which to boot in Flash, perform an Xmodem file transfer.
A typical Xmodem file transfer can take up to 2 hours, which depends on the image size.
Download the Cisco IOS image (.bin file) to which you want to upgrade from the Software Center (Downloads) - LAN Switching Software (registered customers only) .
Note: Do not use a CMS image (.tar file). This image is a larger image and takes longer to transfer.
Issue the dir flash: command in order to compare the size of the image in bytes to the free space that remains in Flash. Here is an example:
If necessary, issue the delete command in order to delete any corrupt images that remain. Here is an example:
The next example shows an Xmodem procedure on a 2955 with the use of HyperTerminal. The procedure is the same for any of the Catalyst fixed configuration switches that this document covers.
Issue the copy xmodem: flash:filename command on the switch.
Here is an example:
From the top of the HyperTerminal window, choose Transfer > Send File.
Choose the Xmodem protocol in the Send File dialog box and click Browse in order to select the Cisco IOS image (.bin file) that you downloaded previously.
Click Send in order to begin the Xmodem transfer.
The Xmodem file transfer begins. This transfer can take up to 2 hours, which depends on the size of the image.
Boot the new image that you just copied over with the Xmodem procedure.
Issue the boot flash:filename command, as this example shows:
Be sure to verify that your boot statements are set correctly.
How to Speed Up Xmodem Recovery
When a user tries to recover the switch from a corrupted or missing IOS, the copy xmodem: flash:[IOS filename] command might not be displayed under the switch: prompt. The copy command might be displayed under the switch: prompt, but not the copy xmodem: command.
Complete these steps in order to speed up the Xmodem recovery:
Set the baud rate to 115200 on the switch: prompt.
Restart HyperTerminal.
Under COM PORT properties, select the bits per second as 115200. The switch: prompt is displayed.
Start the Xmodem recovery.
After the Xmodem recovery, set the BAUD rate back to 9600. If the set BAUD 9600 command does not bring the baud rate to 9600, issue the unset BAUD command in order to bring the baud rate to a default value of 9600 bps.
Verify
Complete these steps:
Issue the show version command in order to verify the current version of software that you run.
Here is an example:
Issue the dir flash:filename command in order to display the Cisco IOS image (.bin file) on a Catalyst 2940, 2950 or 2955.
If you run a CMS image on a Catalyst 2970, 3550, 3560, or 3750, you can store the Cisco IOS image in an image directory. Here is an example:
You may need to issue the dir flash:directory command on a Catalyst 3550 in order to display the Cisco IOS image (.bin file). Here is an example:
Issue the show boot command in order to verify that the boot statement is set correctly.
Here is an example:
Note: Boot statements do not display in the configuration or when you issue the show run command on any of the fixed configuration switches that this document covers. You must issue the show boot command in order to display boot statements.
If no boot statement is set or if the boot statement points to an old or missing version of software, configure the correct boot statement. Issue the boot system flash:filename command.
If you use a CMS image on a Catalyst 2970, 3550, 3560, or 3750, you can store the Cisco IOS image (.bin file) in its own image directory. Issue the boot system flash:directory/filename command. Here is an example: